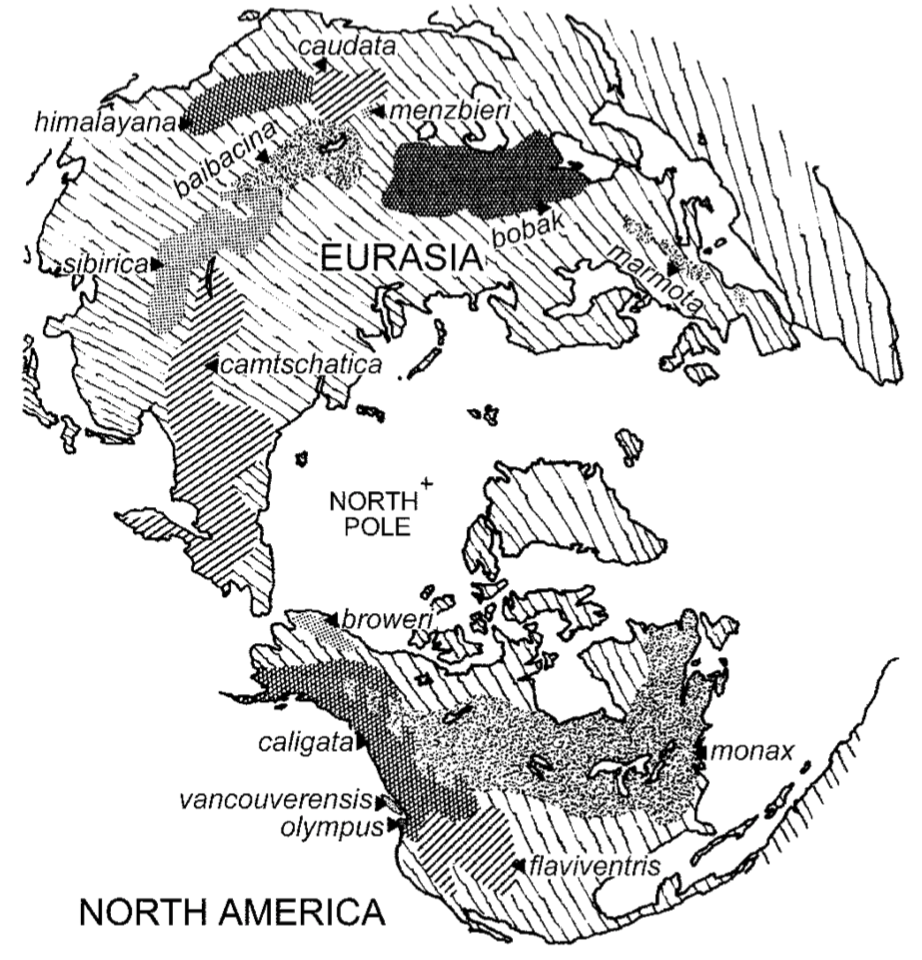
Marmots are large Holarctic rodents in the genus Marmota with 14 living species. Most marmot species occupy a harsh environment characterized by a long, cold season without food. Their physiology is highly adapted to cope with this condition by hibernating in burrows. Global warming since the last ice age has reduced the geographic distribution of some of the marmots. The plagues in some marmots are known to co-occur with human epidemics in the same area, which give rise to a unique surveillance and a major public health concern. MarmotDB database aims to collect the currently available marmots’ genomic data and to characterize the molecular mechanism of hibernating and plague infection by comparisons of the expression profiles from different hibernators and plague hosts or transmitters.
World Marmot
Release notes
- Himalayan marmot genome paper is published in iScience. [January 2019] [Full Text]
- Himalayan marmot genome is publicly accessible. [September 2018]
- Alpine marmot and Yellow-bellied marmot genome are publicly accessible. [December 2017]
- iMarmot Database is available online. [April 2017]